Reliable and fast internet is essential for consumers and organizations in today’s digital environment. The increasing use of fiber optic cables results from the need for quicker, more effective data transmission. These cables are the foundation of contemporary communication networks, renowned for their exceptional performance and sturdiness. This blog will offer a comprehensive installation guide for fiber optic cables, covering everything from the fundamentals to the best practices for a job well done. Whether you’re considering hiring a fiber optic installation company or planning to undertake the task yourself, this comprehensive guide will help you understand the process and make informed decisions.
"*" indicates required fields
Fibre optic cables are a marvel of modern technology, revolutionizing data transmission over long distances. Unlike traditional copper cables, which use electrical signals, fiber optic cables use light to transmit data. This allows for much higher speeds and bandwidths, making them ideal for high-speed internet connections, telecommunications, and data transfer applications.
A typical fiber-optic cable consists of a core, cladding, and protective outer coating. The core, made of glass or plastic, is the medium through which light signals travel. The cladding, made of glass or plastic, surrounds the core and reflects the light into it, preventing signal loss. The outer coating protects the delicate fibers from environmental damage and physical stress.
Fibre optic cables are used in various applications due to their superior performance characteristics. Some of the most common uses include:
Telecommunications: Fibre optic cables form the backbone of modern telecommunications networks, enabling high-speed internet, television, and telephone services.
Data Centers: These cables are essential for data centers, where large amounts of data must be transmitted quickly and reliably between servers and storage devices.
Medical Imaging: Fibre optics are used in medical imaging technologies, such as endoscopy, allowing doctors to see inside the body without invasive surgery.
Military and Aerospace: Fiber optic cables’ high bandwidth and secure nature make them ideal for military and aerospace applications.
Industrial Automation: Fibre optic cables are used in industrial settings to control and monitor machinery and processes with high precision and reliability.
Fibre optic cables transmit data in the form of light pulses. These light pulses are generated by lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and travel through the core of the fiber optic cable. The cladding surrounding the core reflects the light into the core, allowing it to travel long distances with minimal signal loss.
Data is transmitted in binary form, with light pulses representing ones and the absence of light representing zeros. This binary data can be transmitted at incredibly high speeds, making fiber optic cables ideal for applications that require large amounts of data to be transferred quickly and efficiently.
Before beginning the installation process, it is essential to discuss your needs and objectives. Consider the type of data you will transmit, the required bandwidth, and the distance the data will need to travel. This will help you determine the type and specifications of the fiber optic cable you need.
Conducting a thorough site survey is essential to identify potential obstacles and plan the installation. A site survey will help you understand the physical layout of the installation area, identify any possible sources of interference, and determine the best route for the cable.
Identifying the entry point for the fiber optic cable is a crucial step in the installation process. The cable will enter the building or installation area at the entry point. Choosing a location that provides easy access to the main distribution area is essential and minimizes the distance the cable needs to travel.
Planning the cable path involves mapping out the route the cable will take from the entry point to its final destination. Consider factors such as the distance, potential obstacles, and the need for bends and turns. It’s essential to minimize sharp bends and avoid areas where the cable could be damaged or exposed to interference.
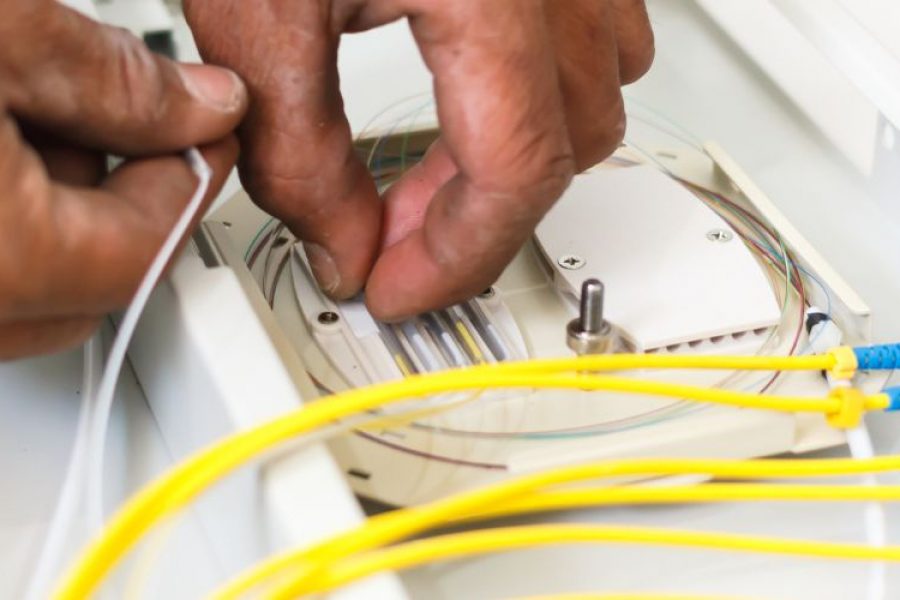
Fiber splicing is the process of joining two fiber optic cables together. There are two main methods of splicing: fusion splicing and mechanical splicing.
Fusion Splicing: This method uses heat to melt the ends of the fibers together, creating a seamless and low-loss connection. Fusion splicing provides the best performance but requires specialized equipment and expertise.
Mechanical Splicing: This method involves aligning the ends of the fibers and holding them together with a mechanical splice. While not as seamless as fusion splicing, mechanical splicing is easier and quicker.
Clear communication with all stakeholders, including building managers, tenants, and local authorities, ensures a smooth installation process. Before beginning the installation, obtain any necessary permits and approvals.
When planning the installation, it’s essential to consider the length of the fiber optic cable. Ensure that the cable is long enough to reach the entry point to the final destination, with some extra length to accommodate any unforeseen obstacles or changes in the route.
A port map visually represents the cable installation, showing the location of ports, connectors, and other vital components. Building a port map will help you plan the installation and ensure all components are correctly connected.
When pulling the fiber optic cable, it’s important to use proper techniques to avoid damaging it. Use a pulling grip to distribute the pulling force evenly, and avoid pulling the cable too tightly around corners or through conduits.
Twisting the fiber optic cable can damage it and cause signal loss. Use proper handling techniques to avoid turning the cable, and ensure it is laid out straight and flat during installation.
Investing in fiber optic cables can provide numerous benefits for your business. Fibre optic cables offer higher speeds, greater bandwidth, and more reliable performance than traditional copper cables. This can improve your business’s productivity, enhance communication, and provide a competitive edge. Fibre optic cables are more durable and require less maintenance, reducing long-term costs.
Network Drops is your trusted partner for professional fiber-optic cable installation. Our team of experienced technicians ensures a seamless, efficient, and secure installation tailored to your specific needs. Whether you’re a small business looking to boost your internet speeds or a large enterprise needing robust data transmission capabilities, Network Drops has the expertise and solutions to meet your requirements. Contact us today for a consultation and discover how we can transform your connectivity. Don’t settle for less—choose Network Drops for top-quality fiber optic installations.
Connecting a fiber optic cable to a connector involves several steps:
Prepare the Cable: Strip the outer coating of the fiber optic cable to expose the core and cladding.
Clean the Fiber: Use a cleaning solution and lint-free wipes to clean the exposed fiber.
Insert the Fiber into the Connector: Carefully insert the cleaned fiber into the connector, ensuring it is appropriately aligned.
Secure the Connector: Use a crimping tool or adhesive to secure the connector in place.
Test the Connection: Use a fiber optic tester to check the connection for signal loss and performance.
Terminating a fiber optic cable involves attaching a connector to the end of the cable. This process typically involves:
Strip the Cable: Remove the outer coating of the cable to expose the core and cladding.
Clean the Fiber: Clean the exposed fiber with a cleaning solution and lint-free wipes.
Prepare the Connector: Open the connector and insert the cleaned fiber into it.
Secure the Connector: Use a crimping tool or adhesive to secure the connector in place.
Test the Connection: Use a fiber optic tester to check the connection for signal loss and performance.
The cost of fiber optic cable can vary depending on several factors, including the type of cable, its length, and its specifications. On average, it ranges from $0.50 to $3.00 per foot. Additional costs may include installation fees, connectors, and other necessary equipment.
Fibre optic cables are used in a variety of applications, including:
Telecommunications: High-speed internet, television, and telephone services.
Data Centers: Connecting servers and storage devices.
Medical Imaging: Technologies such as endoscopy.
Military and Aerospace: Secure and high-bandwidth communication.
Industrial Automation: Controlling and monitoring machinery and processes.
Fibre optic cables offer several advantages over traditional copper cables:
Higher Speeds: Fibre optic cables can transmit data at much higher speeds.
Greater Bandwidth: Fibre optic cables can carry more data over longer distances.
Better Performance: Fibre optic cables are less susceptible to interference and signal loss.
Durability: Fibre optic cables are more durable and require less maintenance.
Security: Fibre optic cables are more secure and less prone to data breaches.
Scott Fcasni is the driving force behind Shock I.T. Support’s commercial datacomm cabling division, delivering expert solutions that power reliable, high-performance network infrastructures. With extensive experience in structured cabling and a commitment to precision, Scott ensures that every project—whether for small businesses or large enterprises—meets the highest standards of quality and scalability.